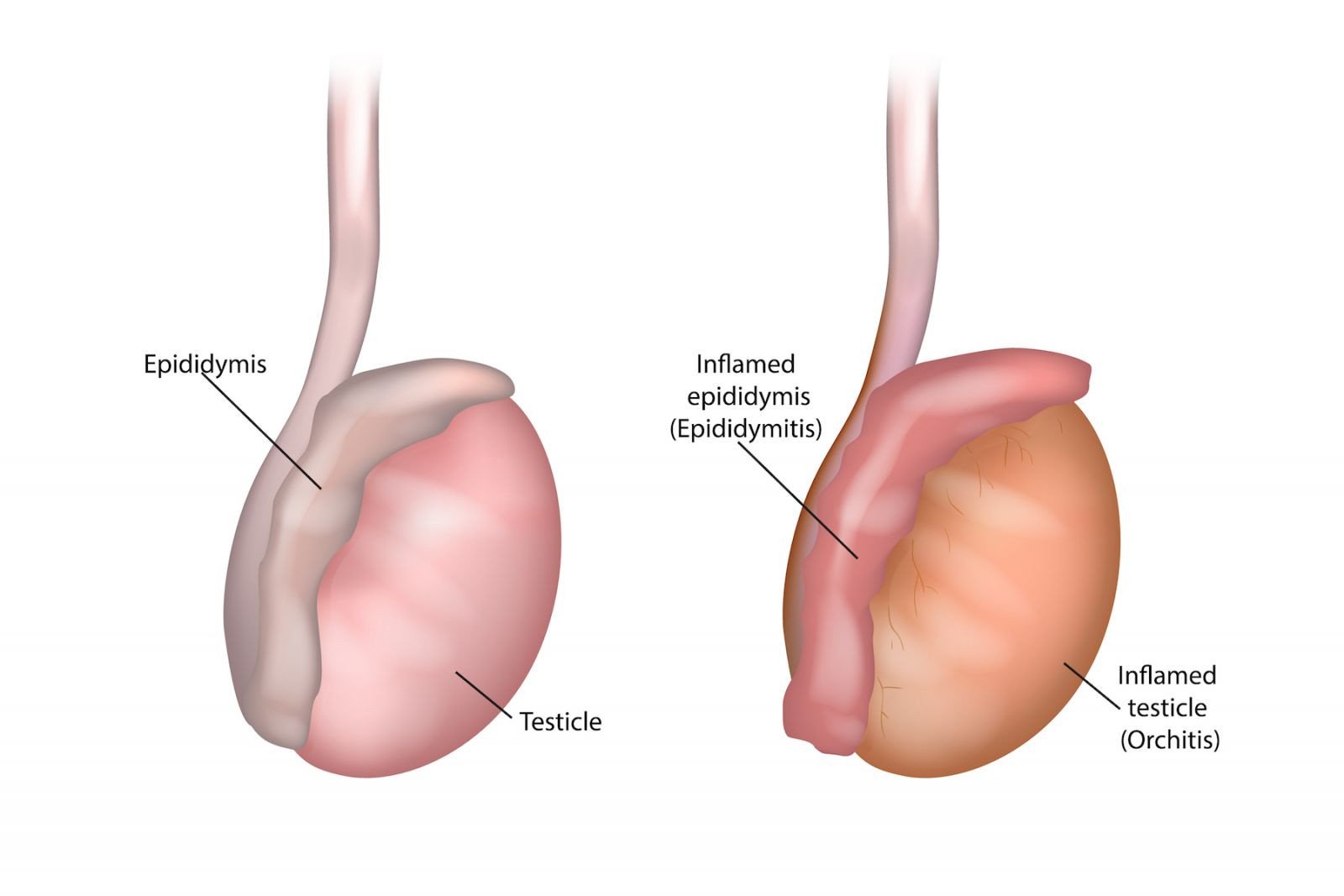
Epididymitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Epididymitis is a medical condition that affects the epididymis, a small tube located at the back of the testicles. This can cause pain during ejaculation and also erectile dysfunction which can force men to take medicines like Cenforce 200 and Vidalista 60. Epididymitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection and can be very painful.
Causes of Epididymitis
Epididymitis is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection, but it can also be caused by a viral infection or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The bacteria that cause epididymitis are usually the same bacteria that cause urinary tract infections (UTIs). The infection can spread to the epididymis through the urethra or the bloodstream.
In some cases, epididymitis can be caused by a blockage in the epididymis or a condition called reflux. Reflux occurs when urine flows backward from the bladder into the epididymis, causing an infection.
Symptoms of Epididymitis
The symptoms of epididymitis can vary depending on the underlying cause of the infection. However, some common symptoms include:
- Pain in the testicles
- Painful urination
- Discharge from the penis
- Blood in the semen
- Pain during ejaculation
- Fever and chills
- A lump on the testicle
- Pain in the groin area or lower abdomen
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of Epididymitis
To diagnose epididymitis, your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms. The doctor may also recommend urine tests for infections. In some cases, imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Epididymitis
The treatment options for epididymitis depend on the underlying cause of the condition. In cases of bacterial infections, antibiotics are typically prescribed to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, may also be recommended to help manage pain and swelling.
In cases of sexually transmitted infections, your sexual partner will also need to be treated to prevent reinfection. It is important to abstain from sexual activity until both you and your partner have completed treatment and the infection has been completely cleared.
If the epididymitis is caused by physical trauma, pain relievers and rest may be recommended to help manage symptoms. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove an abscess or damaged tissue.
Preventing Epididymitis
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing epididymitis. These include:
- Practicing protected sex
- Getting regular checkups for sexually transmitted infections
- Avoiding contact sports or other activities that put the testicles at risk of injury
- Treating urinary tract infections promptly to prevent the spread of bacteria to the epididymis.
Epididymitis is a condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial infections, sexually transmitted diseases, and physical trauma. Common symptoms of epididymitis include pain and swelling in the testicle, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, and difficulty in achieving a firm erection. Treatment options for epididymitis depend on the underlying cause of the condition but men who want to maintain an active sex life are sometimes recommended to take medicines like Fildena 50 and Malegra 200.